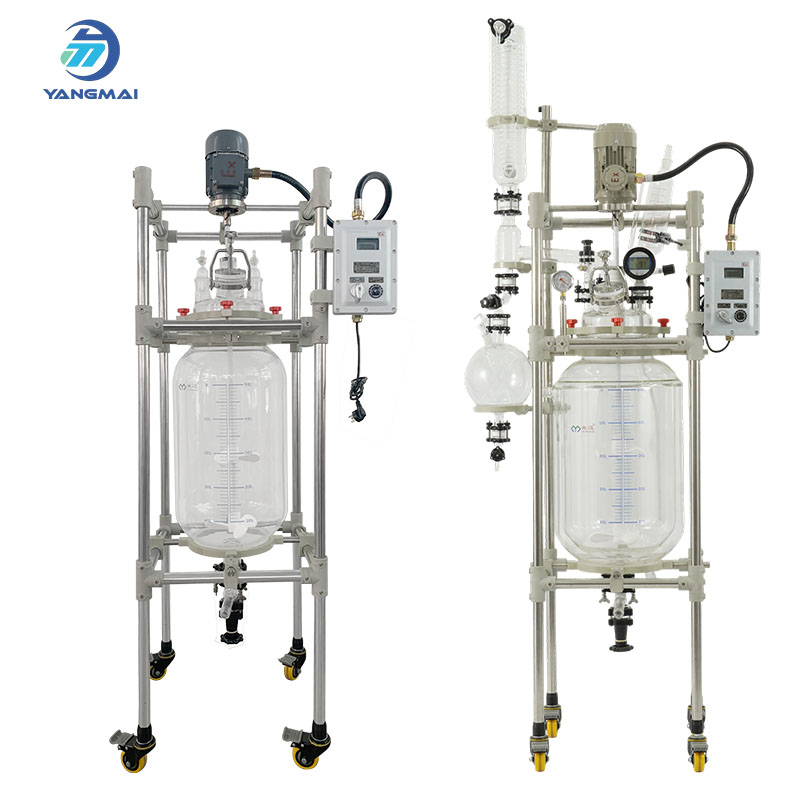
Glass reactors are essential equipment for chemical laboratories, pharmaceutical research, and pilot plant experiments. They provide a controlled environment for chemical synthesis, crystallization, distillation, and solvent recovery.
When selecting a glass reactor, many buyers face the question: Should I choose a single layer glass reactor or a double layer glass reactor? This guide will help you understand the key differences, applications, and criteria for selecting the best reactor for your laboratory or production needs.
What Is a Single Layer Glass Reactor?
A single layer glass reactor is constructed from high borosilicate glass and is typically heated via an oil or water bath. This setup provides direct heating to the reaction vessel, suitable for reactions requiring moderate temperature control.
Key Features:
a. Direct heating via water or oil bath;
b. Compact and easy-to-use design;
c. Supports reactions at atmospheric pressure or mild vacuum;
d. Ideal for small-scale synthesis and laboratory experiments;
Common Applications:
a. Organic synthesis reactions;
b. Stirring and mixing processes;
c. Small-scale crystallization;
d. Solvent evaporation;
What Is a Double Layer Glass Reactor?
A double layer (jacketed) glass reactor features two layers of borosilicate glass, with the interlayer used for circulating heating or cooling fluids such as water, oil, or glycol. This allows precise temperature control for complex chemical processes.
Key Features:
a. Dual-layer glass with thermal fluid circulation;
b. Wide temperature range: -105°C to +300°C;
c. Compatible with vacuum pumps, chillers, and circulation devices;
d. Suitable for medium to large-scale experiments and pilot plant studies;
Common Applications:
a. Pharmaceutical synthesis and production;
b. Fine chemical research;
c. Crystallization, extraction, and distillation under controlled conditions;
d. Scale-up experiments in pilot plants;
How to Choose the Right Glass Reactor?
When deciding between single and double layer reactors, consider:
-
Scale of Experiments
-
Temperature Requirements
-
Budget
-
Application Needs
-
Teaching labs, simple R&D → Single layer
-
Pharmaceutical development, chemical production, scale-up → Double layer
Conclusion
Both single layer and double layer glass reactors are essential tools for laboratories and industrial research. The single layer glass reactor is cost-effective and perfect for small-scale experiments, while the double layer reactor offers precise temperature control and scalability for industrial or pharmaceutical applications.
Choosing the right reactor depends on your experimental scale, temperature requirements, application needs, and budget. Selecting the appropriate reactor ensures efficient, safe, and reproducible chemical processes.
👉 Looking for high-quality single layer or double layer glass reactors? Contact us today for customized solutions and competitive pricing.